M5Atom+PIR UnitをSinric ProでAlexaのモーションセンサーにする
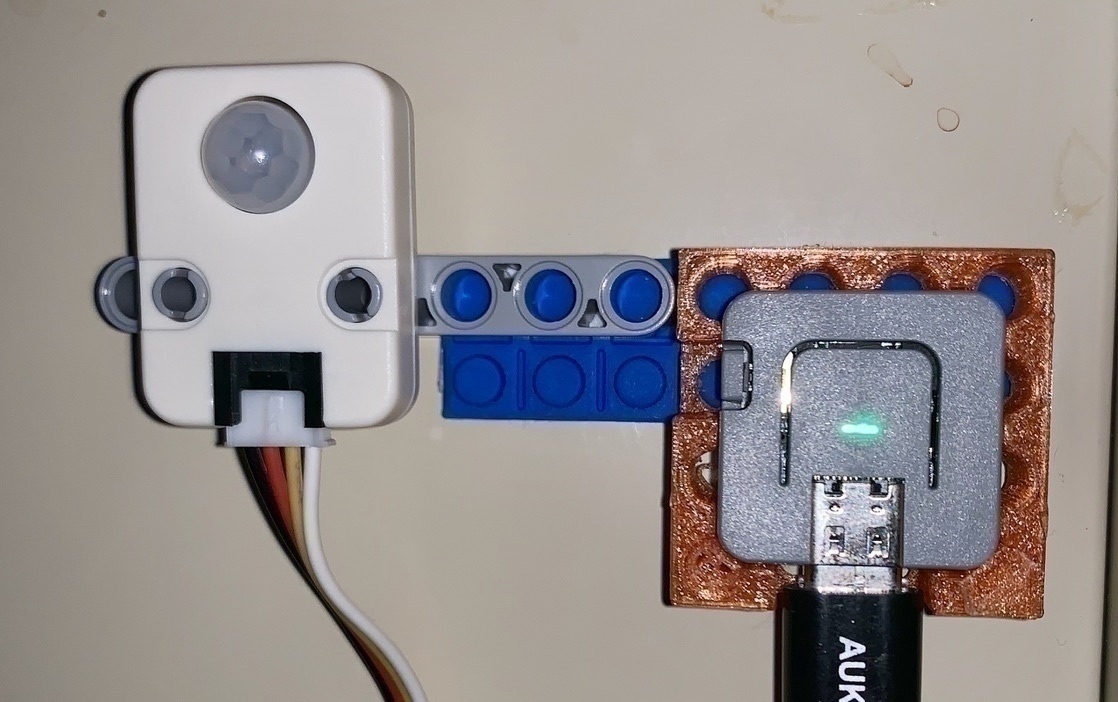
M5Atom Lite とPIRセンサユニット を使って、SwitchBot を動かして照明を人感センサー付きにする、という記事 を最近掲載したばかりですが、実は人感センサーを付けたかったリビングには他にも1つ、赤外線リモコンで操作する照明があって、そちらも同時に人感センサーで制御したいなと思いました。そちらの照明はすでに、SwitchBotハブプラス でAlexa対応しており、SwitchBotもAlexaから制御できるので、このさいM5AtomをAlexaに対応したモーションセンサーにしてしまえば、Alexaの定型アクション 機能を使って、複数の照明を同時に制御できそうです。検索していたら、Sinric Pro という、Raspberry PiやESP32などをAlexaのスマートホームスキルに対応したセンサーやスイッチとして動作させるためのサービスがあったので、そちらを使ってM5Atom + PIRセンサーユニットをAlexaのスマートホームスキルで使えるモーションセンサーにしてみました。
作り方
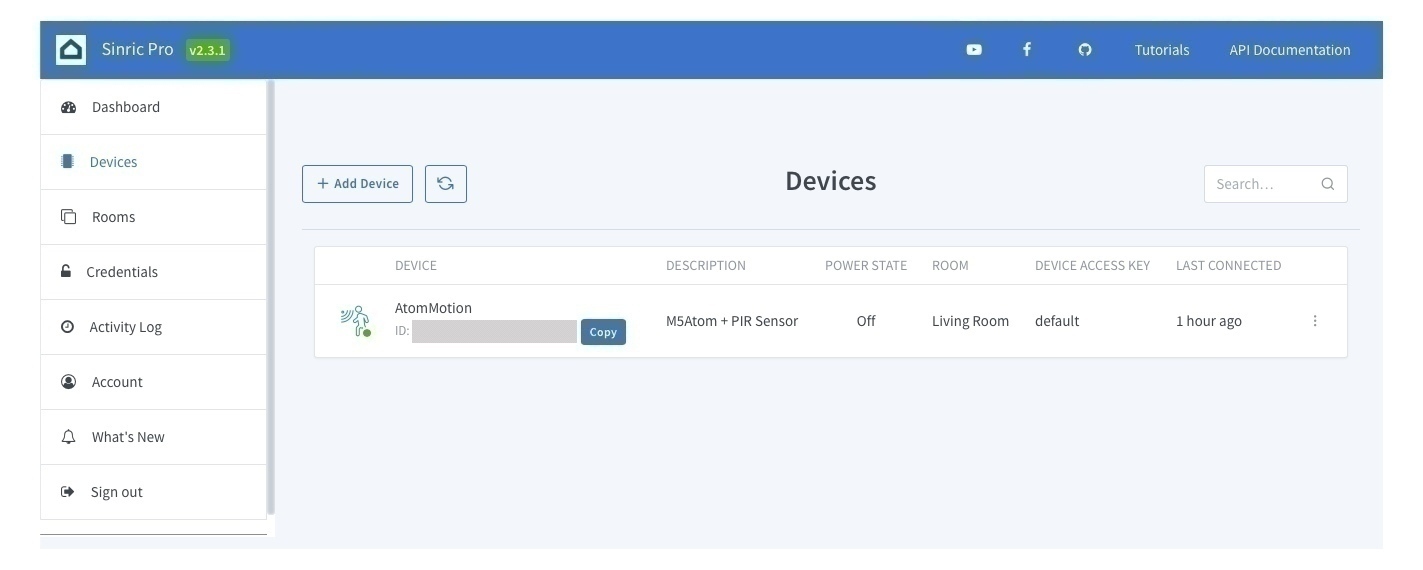
Sinric Proでは、現在のところ5デバイスまでは無料で使えるようです。アカウントを作って、ダッシュボードでデバイスを追加します。追加するときにデバイスタイプを聞かれるので、Motion Sensorを選択しておきます。デバイスIDが発行されるので、それを後ほどArduinoスケッチの中に記載します。
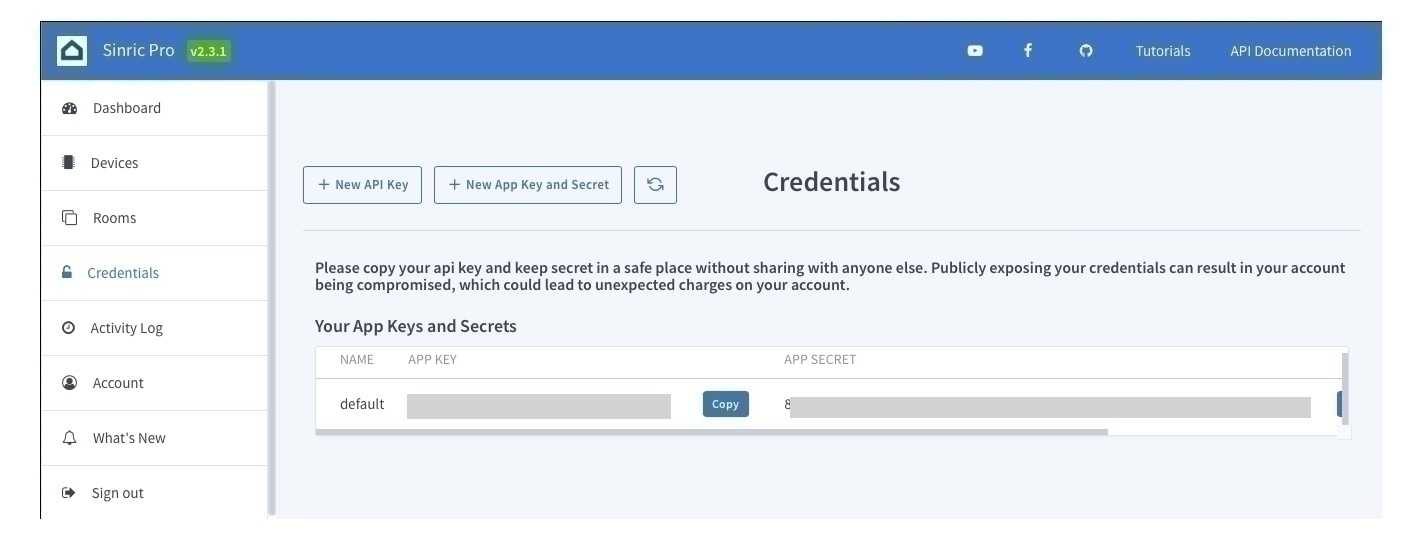
また、アカウントの識別のためのApp Key, App Secretも取得しておき、後ほどスケッチの中に書きます。
あとは、ESP32ベースのデバイスとPIRセンサーを用意すれば、そのデバイスをAlexaのスマートホームスキルのモーションセンサーとして認識されることができます。
スケッチ
いつもどおりGistに置いています。
スケッチはM5Atomのライブラリのほか、Sinric Proのライブラリもインクルードします。これは通常のArduinoのライブラリからインストールできます。
今回はWiFi接続が必要なので、SSIDとパスフレーズをスケッチ中に記載しています。先ほど取得したAPP_KEY, APP_SECRET, それにデバイスID(MOTIONSENSOR_ID) もスケッチ冒頭で記載します。
このスケッチをM5Atomに書き込んだら、あとは電源をつなげるだけで動作しはじめます。前回の工作と同じように、動きを検知しているときはLEDを緑で点灯するようにして、検知していない時は紫にしています。
Alexaへの登録
Alexaのモーションセンサーとして使うには、Sinric ProのAlexaスキル をAlexaで有効にする必要があります。スマートフォンのAlexaアプリなどでこのスキルを有効にしてから、デバイスを検索すると、モーションセンサーが見つかるはずです。あとは、定型スキルのトリガーなどに活用することができます。
感想
今回はBLEなどは使わないので、スケッチもシンプルに書けて、バグに悩まされることもなく一発で期待通りの動作をしました。Sinric Proはよくできていて、ほぼコールバック関数を書くだけでデバイスをAlexa対応にでき、継続して利用していくことができるので、これからもっと使いたいと思います。